Blockchain, crypto, NFTs, the list goes on about web3 development, and if you’re just getting into it now, you must have a ton of questions. It’s no secret that things can get pretty techy in terms of blockchain networks and their inner workings. Don’t worry if you don’t know where to start, the best beginning point is figuring out the technology blockchains have to offer.
Table of Contents
- What Are Blockchains and the Tech Behind Them?
What is a Blockchain?
The biggest appeal of blockchain technologies are transparency (making it easy to validate transactions) and immutability (inability to change). The advanced system allows users to record transactions and track assets easily. It is called a blockchain because it is quite literally what it is – a chain of blocks with data stored, existing within a network.
Each block is set, so what are you left with? An immutable record of transactions that cannot be modified.
Blockchain Unique Features
Blockchain networks offer more than just immutability and transparency, there is also a different philosophy behind them – decentralization.
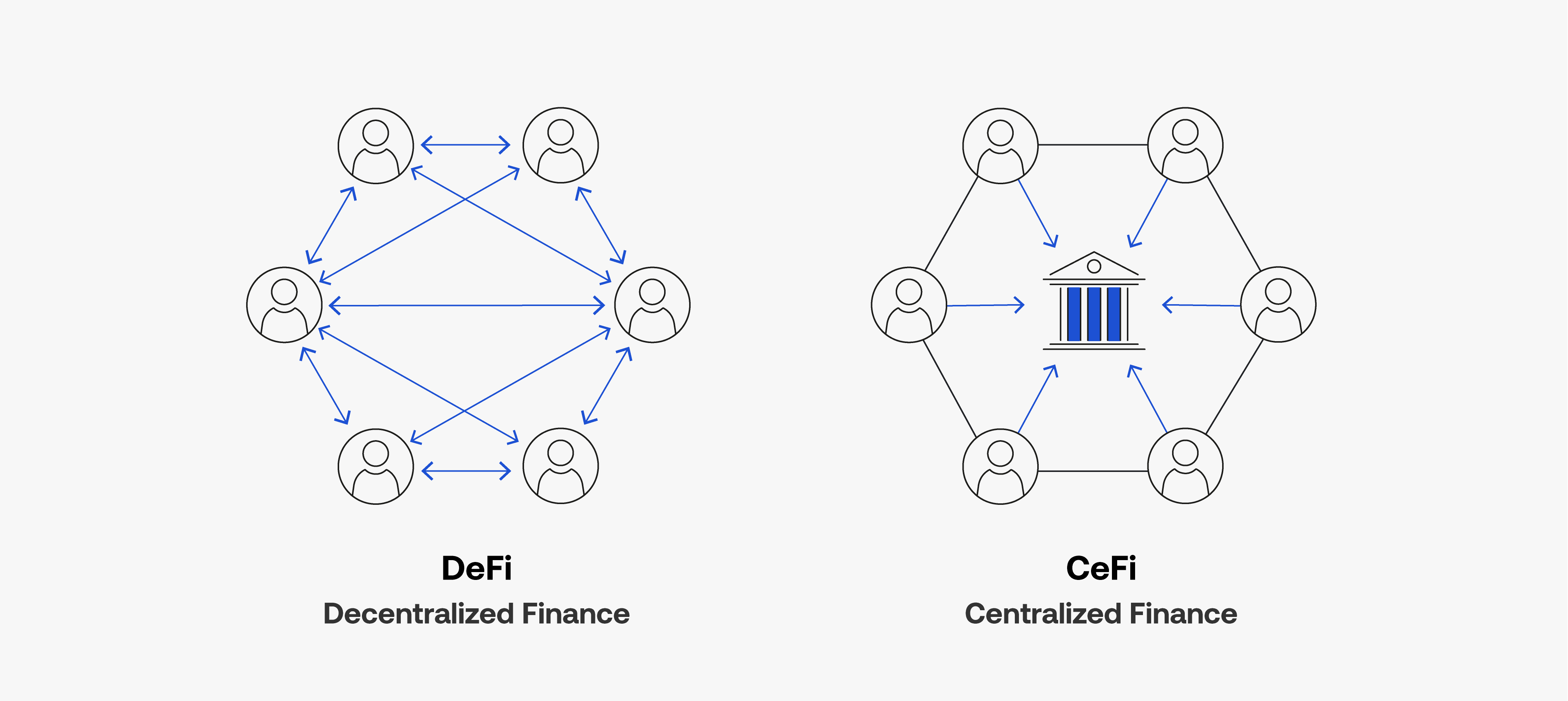
What does this mean? Decentralization means taking control from a single entity and giving it to a network, resulting in distributed “power”. More than one person will get a say in the functionality of the network.
Aside from decentralization and immutability, an entire blockchain also offers consensus. This means that no transactions can be recorded without the consent of the validator.
Blockchain Technology Components
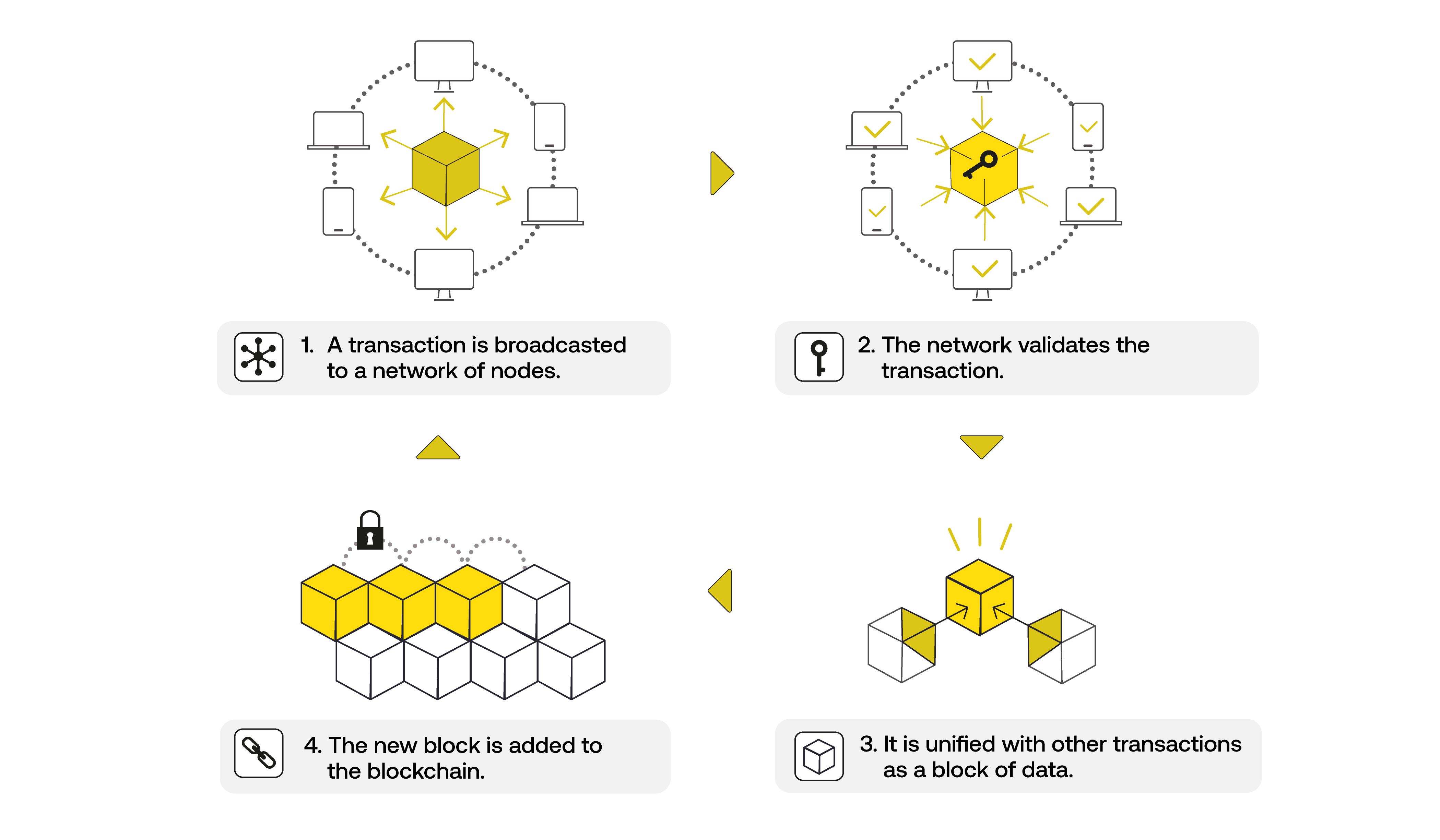
Blockchains feature a few components to make them work: Smart contracts, distributed ledger technology, and public key cryptography.
Smart Contracts
Let’s start with a smart contract. Smart contracts act as an unbiased and automated third party without the actual need for a real third party. A smart contract is a program stored on the blockchain and automatically carries out an action stated in the contract when the predetermined terms are met. It could be as simple as releasing digital assets when payment has been received and vice versa.
Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledger technology refers to the shared database that stores all the information about transactions within a blockchain network. Think of it as a Google document that can be copied by those who have access. However, the rules around who has access within blockchains are highly stringent.
Public and Private Key
Lastly, we have a public and private key. It is basically a security feature used for identification. Typically, a person would have two sets of keys, one private and one public.
The public key is a commonly shared one, while the private one is unique to each individual. In order to access the data within the ledger, a person would need both keys. This further ensures the immutability and security of the blockchain database.
Blockchain Technology Benefits

Okay, so now you have the gist of what blockchain technology is, but what’s the purpose and what does it really offer?
Increased Security and Trust
Real-world financial transactions are not always 100% secure. Mistakes can happen and as the world moves more and more transactions onto digital platforms (crypto being a digital currency), there needs to be strategies in place to guarantee security. A blockchain platform is the first step.
A blockchain eliminates the chances of manipulation, unsanctioned alterations and hacks of transactions. There is no way to fake a transaction and alter the info on the digital ledger at this point (and hopefully never in the future).
Auditing and Efficiency
Blockchains are also a fast way to audit, carry out and validate the transaction. On many networks, you no longer have to wait very long as smart contracts move things along at a much faster pace. Companies and individuals are also able to verify and audit transactions to ensure their validity much quicker than before thanks to the immutable distributed database.
FAQ
What is blockchain technology in simple terms?
A blockchain is a network of data blocks that contain immutable (unchangeable) information relevant to tracking and recording transactions.
What is the main purpose of blockchain?
The main purpose of a blockchain is to provide immutability, decentralization and permissionless transactions.
What is an example of a blockchain?
An example is the Ethereum blockchain. Transactions on this previously proof-of-work blockchain are facilitated by smart contracts encoded into the existing blockchain infrastructure.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, blockchains help improve transparency and immutability, which are also their biggest appeals. It automatically inserts a little more security into a transaction between two strangers that wouldn’t have existed before. Blockchain technology will continue to evolve, especially as we see mass adoption in the future.