Phishing attacks are the most common type of security incident reported by organizations and are still on the rise. They account for more than 80% of all security incidents according to the 2021 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report.
There has also been a huge increase in crypto phishing scam cases in recent years, targeting users of cryptocurrency exchanges, wallets and trading platforms. Losses from crypto scam was a record $14 billion in cryptocurrency, and nearly 1 in 3 phishing emails are opened by their intended recipients. This underscores the importance of awareness and education to help users recognize crypto security and avoid phishing scams.
Table of Contents
What is a phishing scam?
A phishing scam is a type of online fraud that an attacker pretends to be a trustworthy person or organization, and trick you into providing sensitive personal data such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers. Phishing attacks usually take the form of emails, text messages, or phone calls that appear to be from legitimate and reliable sources, such as banks, social media platforms, online retailers, or other types of service providers.
How do phishing scams work?
The goal of a phishing scam is to steal sensitive information from unsuspecting victims, which can then be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or other criminal activities. Criminals may employ many methods to make their phishing attempts look more trustworthy, such as fabricating counterfeit phishing websites that look like the genuine ones, applying social engineering to generate panic or stress, or exploiting the victim’s feelings to earn their assurance.
What would happen if I fell into a phishing scam?
The goal of a phishing scam is to steal sensitive information from unsuspecting victims, which can then be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or other criminal activities. Criminals may employ many methods to make their phishing attempts look more trustworthy, such as fabricating counterfeit phishing websites that look like the genuine ones, applying social engineering to generate panic or stress, or exploiting the victim’s feelings to earn their assurance.
If you fall into a phishing scam and the attackers may have obtained your sensitive personal data, it could lead to a variety of negative consequences, including:
- Financial loss: If the attackers obtain your credit card or bank account details, they may be able to make unauthorized purchases or withdraw funds from your account.
- Identity theft: If the attackers obtain your personal information, ie. your name, address, phone number and government issued identification number, they may be able to open new accounts, take out loans, or conduct other fraudulent activities in your name.
- Malware infection: Some phishing scam may also be designed to install malware or malicious viruses on your computer or mobile device, which can compromise your security and privacy, and potentially lead to further attacks.
- Reputation damage: If the attackers gain access to your social media or email accounts, they may be able to send messages or posts that contain fraudulent contents to your friends and family, and damage your reputation or relationships.
What is a crypto phishing scam?
Crypto phishing scams are a type of phishing attack that specifically targets individuals involved in the cryptocurrency space. In these scams, attackers attempt to steal the victim’s cryptocurrency holdings, private keys, or other sensitive information related to their digital wallets.
How do crypto phishing scams work?
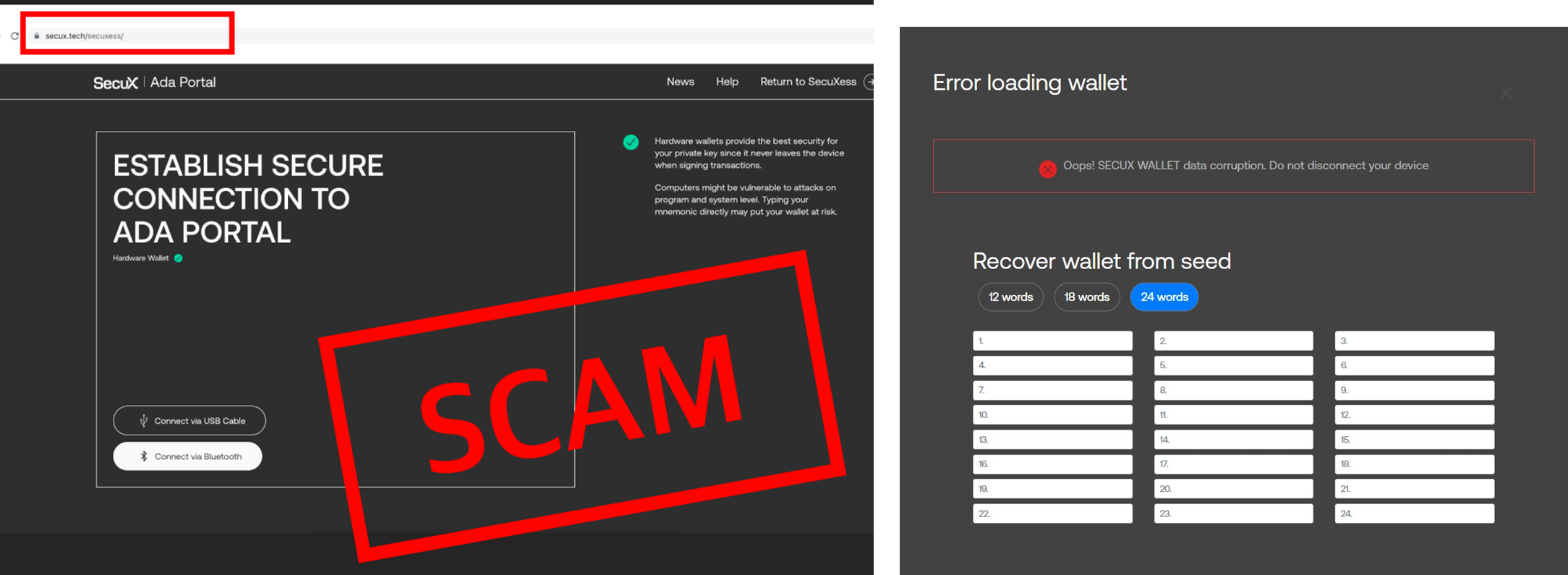
Similar to other phishing scams, a crypto phishing scam typically takes the form of emails, text messages, or social media posts that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a cryptocurrency exchange, wallet provider, or trading platform. The messages often contain a link to a fake website that closely resembles the real one, and may prompt the victim to enter their login credentials or other sensitive information.
IMPORTANT!! SecuX will never ask for your 24 recovery words, recovery seed phrase or your private key information. Never share them with anyone, not even SecuX.
Once the victim has entered their information, the attackers can use it to access their crypto wallet and steal their funds. In some cases, the attackers may also use the stolen information to conduct identity theft or other fraudulent activities. For example, an attacker may illegally obtain access as a discord channel admin, and post fake airdrop information to the community.
The popularity of such an event may be used to deceive people into connecting their crypto wallets to a malicious website in which their private keys and other personal information can be stolen. Attackers can then use this information to gain access to the user’s digital assets, such as cryptocurrency, NFTs, and other forms of digital property.
Beware of 6 common types of crypto phishing scams
There are several different types of crypto phishing scams, but they all generally involve tricking users into giving up their private key, recovery seed phrase or wallet login information.
Here are 6 common types of crypto phishing scams:
- Fake websites: Scammers create fake websites that look like legitimate crypto wallets or cryptocurrency exchanges. Users may think they are accessing the legitimate service as usual, but in fact mistakenly enter their login credentials, wallets addresses, public or private keys into the fake website.
- Social media scams: Scammers create fake social media profiles or hack legitimate ones to spread phishing links. They may also impersonate legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or crypto wallet providers to trick users into giving them sensitive information by offering customer service or troubleshooting their account issues.
- Phishing emails: Scammers send emails that look like they are from legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or crypto wallet providers, but contain links to fake websites. The URLs for such fake websites often look very similar to the real ones by reordering a couple of letters.
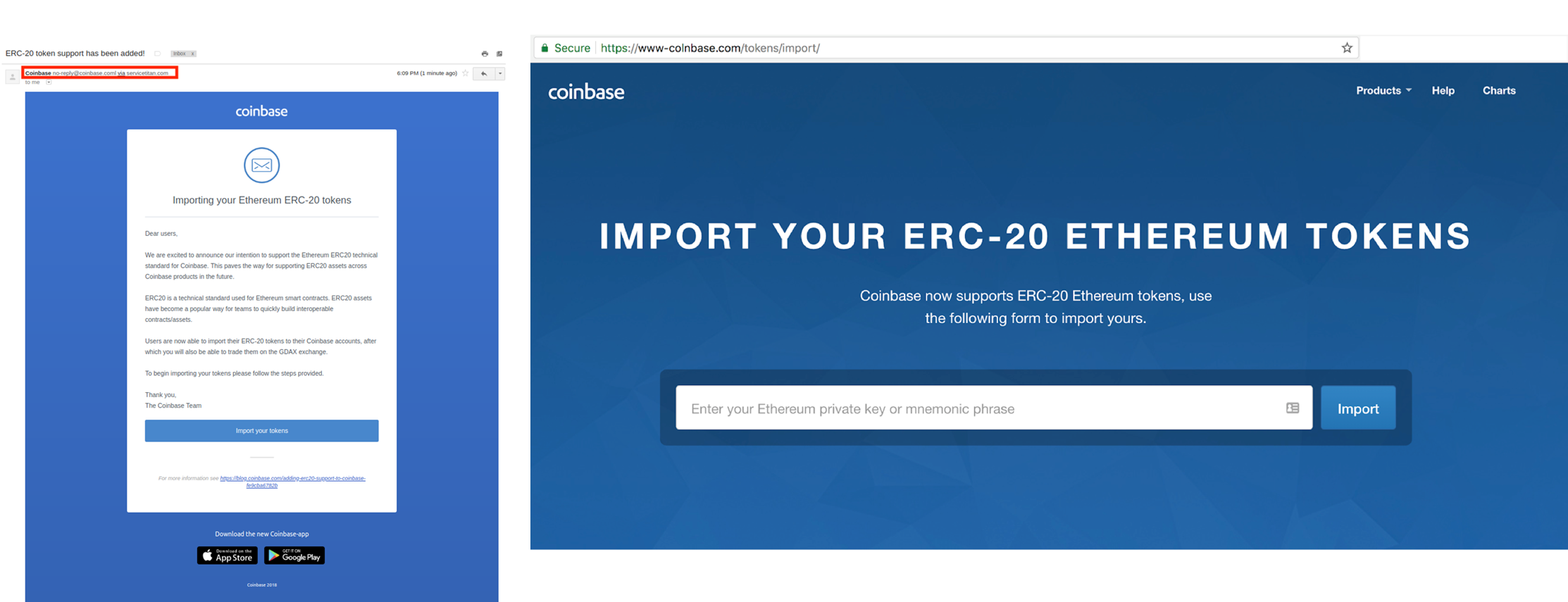
- Mobile app scams: Scammers create fake mobile apps that look like legitimate crypto exchanges or cryptocurrency wallets. Users may download these apps the unknowingly give the scammers access to their cryptocurrency and digital assets.
- Fake ICOs, NFT rug pull or fake airdrops: Scammers may promise high returns or exclusive access to a new cryptocurrency, NFT project or airdrops to specific NFT or token holders. They may trick investors into sending them cryptocurrency, but then have no intention of delivering anything.
- Crypto giveaways: Scammers may pose as well-known figures in the cryptocurrency and NFT industry and offer to give away cryptocurrency in exchange for a small fee in fiat or cryptocurrency. However, the victims may not receive any crypto in return.
How to avoid crypto phishing scams?
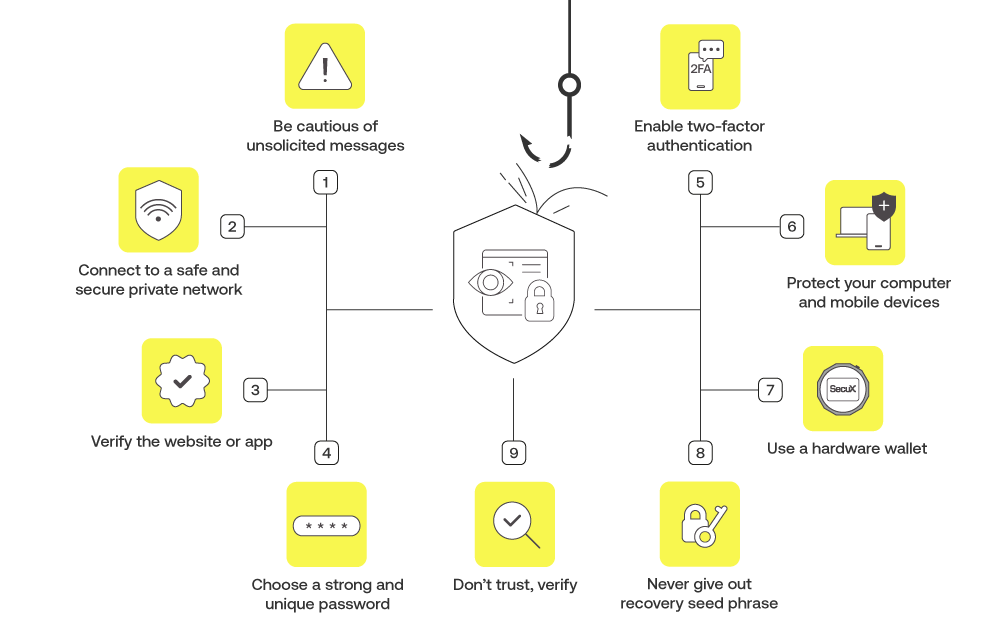
Here are 9 steps you can take to avoid falling victim to a crypto phishing scam:
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages: If you receive an unsolicited message from someone you don’t know or a company’s email address you don’t recognize, be cautious, and don’t click on any links or download any attachments.
- Connect to a safe and secure private network: Scammers may try to hack into your computer or mobile devices from a public and unsecure network. Keep out of reach from malicious attackers by only connecting to a safe and secure private network.
- Verify the website or app: Before entering any sensitive information, make sure that the website or app you are using is legitimate. Look for signs of a secure connection, such as a lock icon in the browser address bar and “https” in the URL. Always double check the spelling of the URL of websites and app download links before clicking.
- Choose a strong and unique password: Use a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols, and make it at least 12 characters long. Avoid easily guessable passwords such as “123456”, or personal information including your name, date of birth or phone number.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password. This makes it harder for scammers to access your cryptocurrency or sensitive information.
- Protect your computer and mobile devices: Install reputable antivirus software to help detect and remove viruses and malware. Keep your operating systems, web browsers and other softwares up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Use a hardware wallet: A hardware wallet, or a cold wallet is a physical cold storage device that stores your cryptocurrency offline. It keeps out malware and viruses that could steal private key information from your computer or mobile phone when using a hot wallet. This makes it very difficult for scammers to access your funds, even if they have your login credentials.
- Never give out recovery seed phrase or private key, and keep them in a safe place: Your private key opens complete access to your crypto funds and collectibles such as NFTs. Never share them online, or with anyone. Reliable hardware wallet providers such as SecuX, would never ask you for your recovery words, recovery seed phrase or private key. It is also important to keep them safe in case of loss or damage.
- Don’t trust, verify: Stay informed about the latest crypto phishing scams and how to avoid them. Always verify sellers’, organizations’ or service providers’ social media accounts or emails, and cross-check prices and other information to identify their legitimacy. Remain suspicious, trust no one, and do not act before you verify.
Conclusion
It’s important to be vigilant and cautious when receiving emails, messages, or calls from unknown or suspicious sources, and to never provide sensitive information, unless you are absolutely sure that the request is legitimate. For crypto users, always do your own research (DYOR) and due diligence before investing, never share your private key or recovery seed phrase online, choose a secure hardware wallet and keep your private key / seed phrase information offline.
Don’t trust, verify.